Essential AI Reports for Business Leaders: Stanford AI Index Annual Report 2024
Stay updated with the latest AI trends with in-depth analysis of the Stanford AI Index Annual Report 2024. Discover crucial advancements in LLMs, generative AI, and regulatory changes.
Hello folks! I'm excited to continue our series on Essential AI Reports for Business Leaders. The AI revolution is showing no signs of slowing down, and staying ahead of the curve is crucial for anyone in the business world.
Today, I want to shift our focus to a stunning 502 pages report from a truly authoritative source: the Stanford AI Index Annual Report 2024. This report offers a unique and comprehensive perspective on the global impact of AI, providing valuable data and insights into its technical advancements, societal implications, and geopolitical dynamics.
Join me as I want to read the key findings of this report with you today, exploring how AI is transforming industries, shaping public opinion, and influencing the global landscape. If you missed the previous entries in this series, be sure to check them out to get a well-rounded view of the AI landscape:
Top 10 AI Takeaways in 2024
First, we follow the official part with broader overview.
AI beats humans on some tasks, but not on all.
AI has surpassed human performance on several benchmarks, including some in image classification, visual reasoning, and English understanding. Yet it trails behind on more complex tasks like competition-level mathematics, visual commonsense reasoning and planning.
Industry continues to dominate frontier AI research.
In 2023, industry produced 51 notable machine learning models, while academia contributed only 15. There were also 21 notable models resulting from industry-academia collaborations in 2023, a new high.
Frontier models get way more expensive.
According to AI Index estimates, the training costs of state-of-the-art AI models have reached unprecedented levels. For example, OpenAI’s GPT-4 used an estimated $78 million worth of compute to train, while Google’s Gemini Ultra cost $191 million for compute.
The United States leads China, the EU, and the U.K. as the leading source of top AI models.
In 2023, 61 notable AI models originated from U.S.-based institutions, far outpacing the European Union’s 21 and China’s 15.
Robust and standardized evaluations for LLM responsibility are seriously lacking.
New research from the AI Index reveals a significant lack of standardization in responsible AI reporting. Leading developers, including OpenAI, Google, and Anthropic, primarily test their models against different responsible AI benchmarks. This practice complicates efforts to systematically compare the risks and limitations of top AI models.
Generative AI investment skyrockets.
Despite a decline in overall AI private investment last year, funding for generative AI surged, nearly octupling from 2022 to reach $25.2 billion. Major players in the generative AI space, including OpenAI, Anthropic, Hugging Face, and Inflection, reported substantial fundraising rounds.
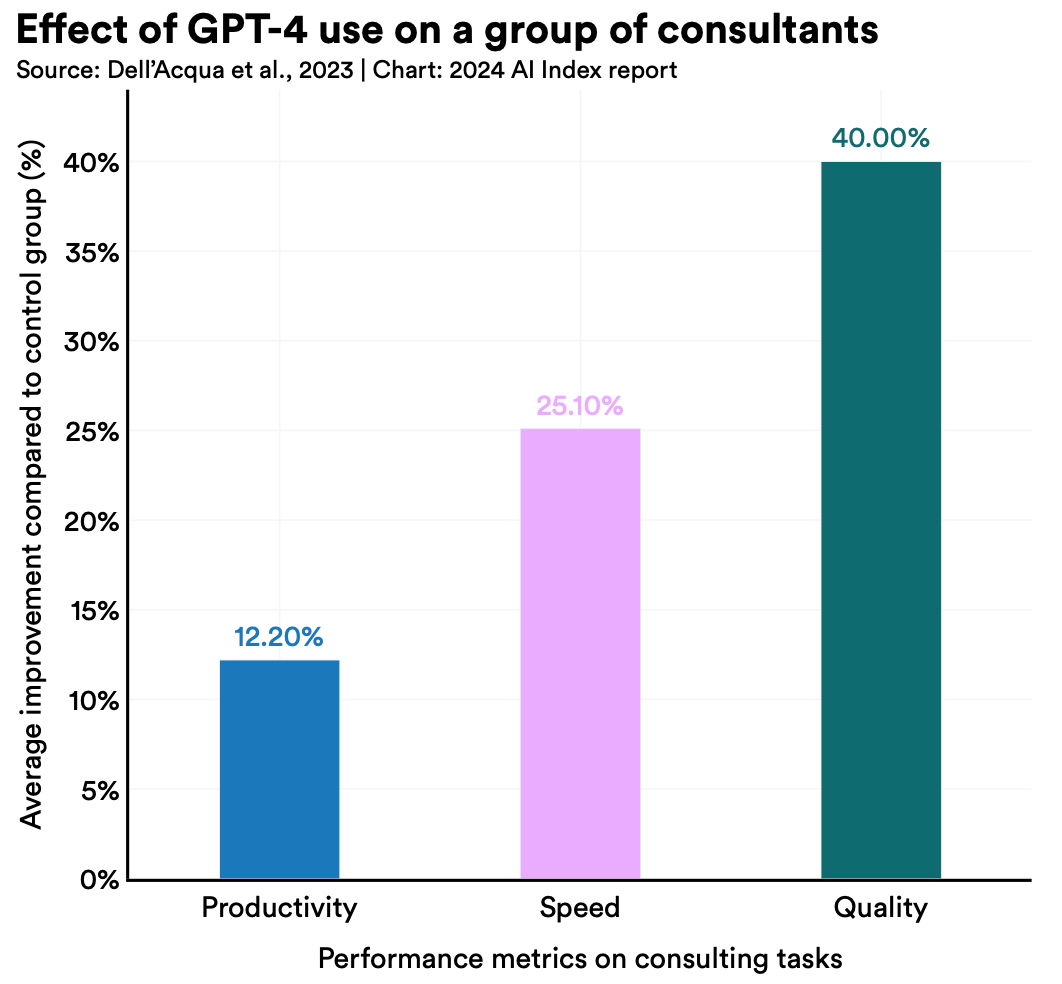
The data is in: AI makes workers more productive and leads to higher quality work.
In 2023, several studies assessed AI’s impact on labor, suggesting that AI enables workers to complete tasks more quickly and to improve the quality of their output. These studies also demonstrated AI’s potential to bridge the skill gap between low- and high-skilled workers. Still, other studies caution that using AI without proper oversight can lead to diminished performance.
Scientific progress accelerates even further, thanks to AI.
In 2022, AI began to advance scientific discovery. 2023, however, saw the launch of even more significant science-related AI applications— from AlphaDev, which makes algorithmic sorting more efficient, to GNoME, which facilitates the process of materials discovery.
The number of AI regulations in the United States sharply increases.
The number of AI related regulations in the U.S. has risen significantly in the past year and over the last five years. In 2023, there were 25 AI-related regulations, up from just one in 2016. Last year alone, the total number of AI-related regulations grew by 56.3%.
People across the globe are more cognizant of AI’s potential impact—and more nervous.
A survey from Ipsos shows that, over the last year, the proportion of those who think AI will dramatically affect their lives in the next three to five years has increased from 60% to 66%. Moreover, 52% express nervousness toward AI products and services, marking a 13 percentage point rise from 2022. In America, Pew data suggests that 52% of Americans report feeling more concerned than excited about AI, rising from 37% in 2022.
My Personal Key Takeaways from the Stanford AI Index Annual Report 2024
Beyond the comprehensive overview, a few specific findings from the report really caught my attention:
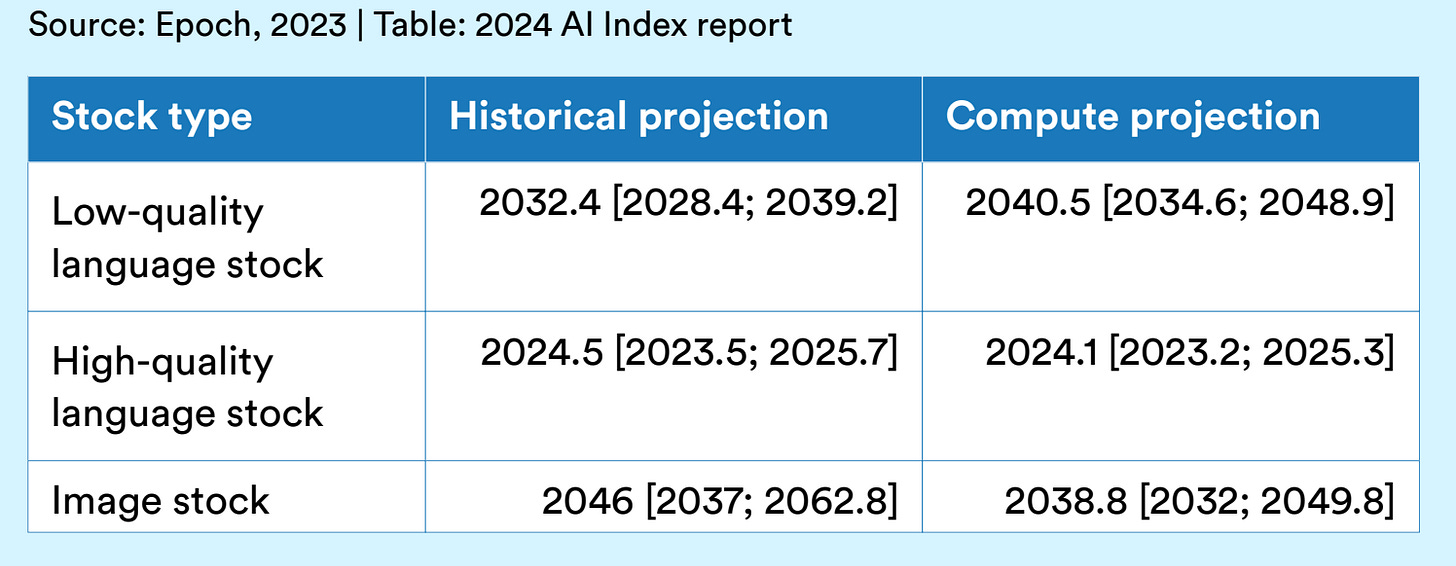
Models can run out of training data. This is a real concern raised by Anthropic's co-founder. The report suggests that high-quality language data could be depleted as early as 2024. This could be a significant bottleneck in AI development, but the assumption is that we continue the journey using the synthetic data already trained models could output.
The rising popularity of open-source AI projects on platforms like GitHub highlights the democratization of AI development. The geographical distribution of contributions shows that AI innovation is a global phenomenon, not limited to a few tech hubs. Since 2011, the number of AI-related GitHub projects has seen a consistent increase, growing from 845 in 2011 to approximately 1.8 million in 2023.
Despite the impressive Devin AI failure, the coding capabilities of LLMs have improved significantly, leading researchers to create even newer, more complex benchmarks to evaluate coding capabilities. In October 2023, researchers introduced SWE-bench, a dataset comprising 2,294 software engineering problems sourced from real GitHub issues and popular Python repositories. The growth in this area promises that coding will definitely become a routine task someday.
Today's image generators are so advanced that most people struggle to differentiate between AI-generated images and actual images of human faces. But that's not all: 3D model generation and 3D image reconstruction are the new trends. Generation of 3D models from text prompts is becoming a reality – MVDream is a new 3D generation system developed by ByteDance and University of California, San Diego researchers that overcomes some of these hurdles. Also, 3D image reconstruction is the process of creating three-dimensional digital geometries from two-dimensional images – a team of international researchers introduced an extensive new dataset, Skoltech3D, for multiview 3D surface reconstruction. RealFusion, developed by Oxford researchers, is a new method for generating complete 3D models of objects from single images, overcoming the challenge of often having insufficient information from single images for full 360-degree reconstruction. RealFusion utilizes existing 2D image generators to produce multiple views of an object and then assembles these views into a comprehensive 360-degree model.
Improved reasoning across multiple fields – a growing trend in AI research. General reasoning focus on enhancing reasoning capabilities across multiple domains. Abstract reasoning on solving novel problems with known limited information. Mathematical reasoning continue to advance in complex math problems. Visual reasoning focus on getting the new information from videos an images. And finally, the moral reasoning where ethical considerations are crucial. These advancements promise to make AI systems more adaptable and capable of solving complex, real-world challenges.
Political bias is inherent in some LLMs, as evidenced by research on ChatGPT's responses, raise concerns about their potential to shape users' political views. While LLMs are increasingly valuable tools for learning about political topics, the biases they exhibit can disproportionately align with certain political ideologies. This could inadvertently influence users potentially impacting their decision-making in both political and daily life.

Graph shows strong positive correlations (blue lines) between the default ChatGPT, i.e., one that was answering questions without additional instructions, and both the Democrat and the radical Democrat ChatGPT versions, i.e., versions of ChatGPT that were asked to answer like a Democrat or radical Democrat One of the top concerns when discussing AI’s impact on political processes is the generation of disinformation. A developer called Nea Paw set up an experiment in creating a fully automated disinformation pipeline. The entire setup for this authentic-appearing misinformation system only cost around $400 and had a huge impact on media.
Across all regions, the adoption rate of generative AI by organizations stands at 33%. As an outcome most early adopters have experienced both cost reductions and revenue increases due to AI adoption.
AI is making HUGE changes in science and medicine – a ton of impressive things are happening in medicine and science. AI is helping medicine take significant strides forward. Highly knowledgeable medical AI has arrived – sort of like ChatGPT but focused on medicine. The FDA is approving more and more AI-related medical devices. As an example:
scientists from the Human Pangenome Research Consortium, used AI to develop an updated and more representative human genome map;
Researchers from Google DeepMind unveiled AlphaMissense, a new AI model that predicted the pathogenicity of 71 million missense variants as scientists still do not fully understand which genetic mutations lead to diseases.;
EVEscape is a new AI deep learning model trained on historical sequences and biophysical and structural information that predicts the evolution of viruses;
A new method for neurodegenerative disease (such as Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s) diagnosis that combined AI-coupled plasmonic infrared sensors that use Surface-Enhanced Infrared Absorption (SEIRA) spectroscopy with an immunoassay technique.
The rise of LLMs also has sparked discussions about their use in education. Concerns about plagiarism have led to calls for rethinking how American students are taught. A study by Impact Research found that a majority of U.S. teachers are using ChatGPT and, from March to July 2023, usage increased from 51% to 63% of teachers.
The data from various industries indicates a notable increase in hiring for AI-related roles. Particularly, industries like financial services and tech, media, and telecom sectors have shown a high demand for it. This trend highlights that the expansion of AI is not only advancing technology but also creating more job opportunities across different sectors.
Well, folks, that wraps up our highlights into the Stanford AI Index Annual Report 2024. If you're interested in catching up with the latest trends or simply want a comprehensive overview, this report is an excellent opportunity to do so – it highlights all major developments, trends, possibilities, and much more – all the information you will ever need to make informed decisions and stay in the loop.
Thank you for joining me on this enlightening journey. Stay curious, stay informed, and as always, let's embrace the future together.
🔎 Read the full report to stay in the loop: Artificial Intelligence Index Report 2024