The Ultimate Cheat Sheet for Mastering AI Chatbots
The One and Only Guide for Advanced Techniques in Prompt-Engineering
Hello folks, today I found another great study that I would like to share with you. As a professional in the IT world, I'm always on the lookout for groundbreaking research that can transform the way we interact with technology. Recently, I stumbled upon a gem - a study that unveils the ‘26 Rules’ for mastering AI chatbots.
This is more than just another guide; it's research that we can rely on with a considerable degree of certainty. This is especially true in 2024, as AI chatbots become increasingly sophisticated and integral to our digital lives.
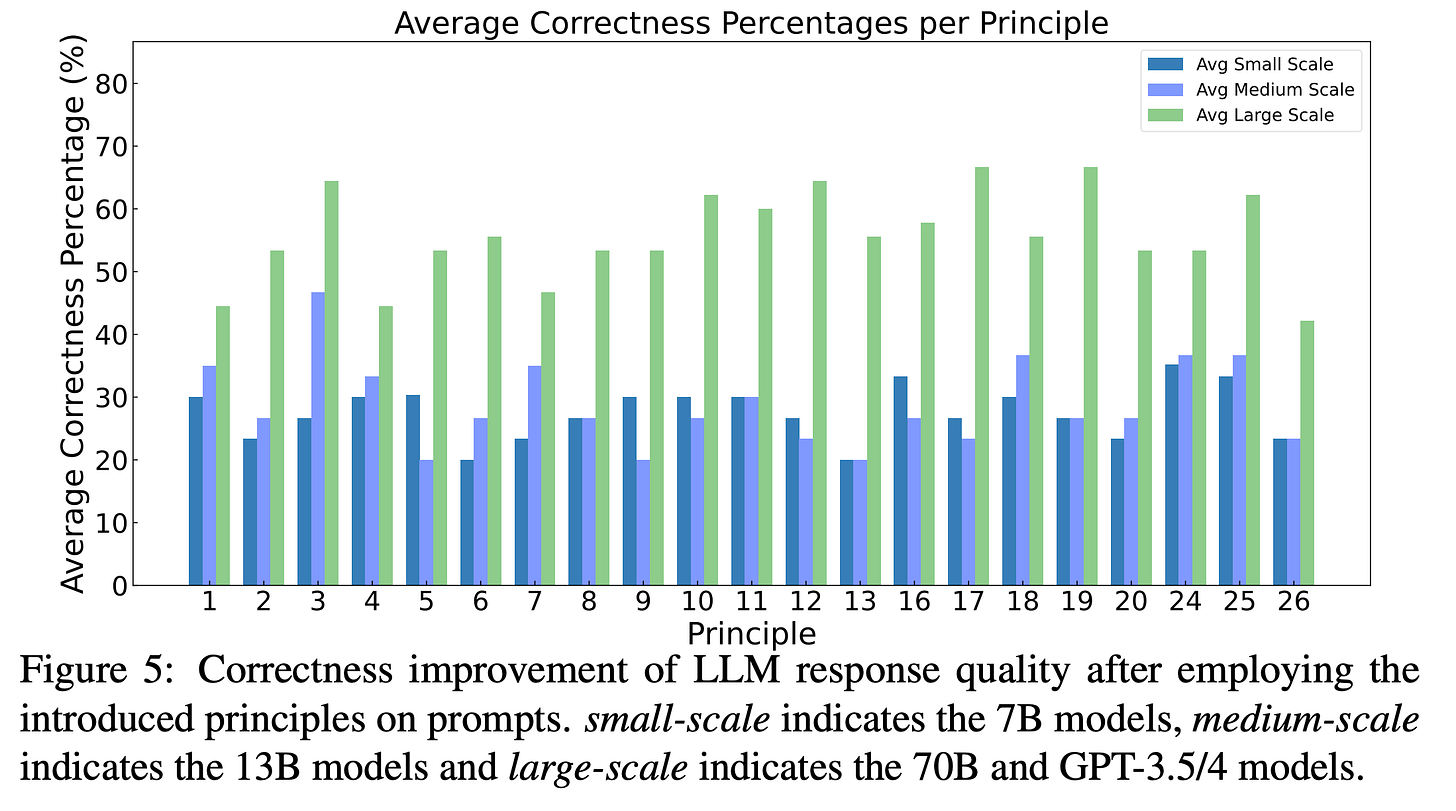
The study, conducted by the VILA Lab at Mohamed bin Zayed University of Artificial Intelligence in Abu Dhabi, is a deep dive into the nuances of prompt-engineering – the art of effectively communicating with large language models (LLMs). Their findings results in a compelling piece of research titled “Principled Instructions Are All You Need for Questioning LLaMA-1/2 GPT-3.5/4”, further emphasising the importance of these principles.
Key Takeaways from the Research
Simplicity and Clarity: The study emphasizes the importance of clear and straightforward prompts, a principle echoed in the “26 Rules”. Clarity leads to more focused responses from AI.
Specificity is Key: Being specific in our queries significantly improves the relevance and accuracy of AI responses.
The Art of Prompt Structure: The way we frame our questions can make a world of difference. This is particularly evident in complex tasks, where breaking down the query into manageable parts leads to better results.
Engagement and Interaction: How we engage with AI determines the quality of the output. The research and the ‘26 Rules’ both highlight the importance of this dynamic interaction.
The rules are not just a set of instructions; they are a philosophy for AI interaction. This is crucial because, as the study highlights, the quality of our interactions with AI largely depends on how we frame our questions and prompts. It reminded me of my earlier article, where we discussed the topic: Can AI truly mimic emotional intelligence? The experiments showed, for example, that if you add to the end of a chatbot's prompt (task setting) the phrase "this is very important for my career", its response noticeably improves:
Applying the Rules
In testing these rules with various AI models, including GPT-3.5/4, I witnessed remarkable improvements. Complex queries that once stumped these models are now answered with a surprisingly higher level of accuracy and depth. These guidelines might not only deepen your understanding of AI but also vastly improve the efficiency and quality of your interactions with these systems.
Prompt Structure and Clarity
Integrate the intended audience in the prompt;
Employ affirmative directives such as ‘do’ while steering clear of negative language like ‘don’t’;
Use Leading words like writing “think step by step.”;
Use output primers, which involve concluding your prompt with the beginning of the desired output. by ending your prompt with the start of the anticipated response;
Use Delimiters;
When formatting your prompt, start with ‘###Instruction###’, followed by either ‘###Example###’ or ‘###Question###’ if relevant. Subsequently, present your content. Use one or more line breaks to separate instructions, examples, questions, context, and input data;
Specificity and Information
Implement example-driven prompting (Use few-shot prompting);
When you need clarity or a deeper understanding of a topic, idea, or any piece of information, utilize the following prompts:
Explain [insert specific topic] in simple terms;
Explain to me like I’m 11 years old o Explain to me as if I’m a beginner in [ field ];
“Write the [essay/text/paragraph] using simple English like you’re explaining something to a 5-year-old”;
Add to your prompt the following phrase “Ensure that your answer is unbiased and does not rely on stereotypes.”;
To write any text intended to be similar to a provided sample, include specific instructions:
“Please use the same language based on the provided paragraph.[/title/text /essay/answer]”;
When you want to initiate or continue a text using specific words, phrases, or sentences, utilize the provided prompt structure:
I’m providing you with the beginning [song lyrics/story/paragraph/essay...]: [Insert lyrics/words/sentence]. Finish it based on the words provided. Keep the flow consistent.
Clearly state the model’s requirements that the model must follow in order to produce content, in form of the keywords, regulations, hint, or instructions;
To inquire about a specific topic or idea and test your understanding, you can use the following phrase:
“Teach me the [Any theorem/topic/rule name] and include a test at the end, but don’t give me the answers and then tell me if I got the answer right when I respond”;
To write an essay/text/paragraph/article or any type of text that should be detailed:
“Write a detailed [essay/text/paragraph] for me on [topic] in detail by adding all the information necessary.”;
User Interaction and Engagement
Allow the model to elicit precise details and requirements from you by asking you questions until he has enough information to provide the needed output:
“From now on, I would like you to ask me questions to...”;
To write an essay /text /paragraph /article or any type of text that should be detailed: “Write a detailed [essay/text/- paragraph] for me on [topic] in detail by adding all the information necessary”;
Content and Language Style
To correct/change specific text without changing its style: “Try to revise every paragraph sent by users. You should only improve the user’s grammar and vocabulary and make sure it sounds natural. You should not change the writing style, such as making a formal paragraph casual.”;
Incorporate the following phrases: “Your task is” and “You MUST.”;
Incorporate the following phrases: “You will be penalized.”;
Assign a role to the language model;
Use the phrase “Answer a question given in natural language form” in your prompts;
No need to be polite with LLM so there is no need to add phrases like “please”, “if you don’t mind”, “thank you”, “I would like to”, etc., and get straight to the point;
Repeat a specific word or phrase multiple times within a prompt;
Add “I’m going to tip $xxx for a better solution!”;
Complex Tasks and Coding Prompts
Break down complex tasks into a sequence of simpler prompts in an interactive conversation;
When you have a complex coding prompt that may be in different files:
“From now and on whenever you generate code that spans more than one file, generate a [programming language] script that can be run to automatically create the specified files or make changes to existing files to insert the generated code. [your question].”;
Combine Chain-of-thought (CoT) with few-shot prompts;
Embracing the Future of AI Communication
As we forge ahead in the 21st century, mastering prompt-engineering is not just a skill but a necessity for anyone interested in AI. This “26 Rules” are a blueprint for effective AI communication. I urge you to explore these rules. Understand them, apply them, and watch as your interactions with AI transform.
The journey with AI just only started. Stay curious, keep experimenting, and embrace the endless possibilities these advancements offer.
Stay tuned for more insights, and happy prompt-engineering!
🔍 Explore more